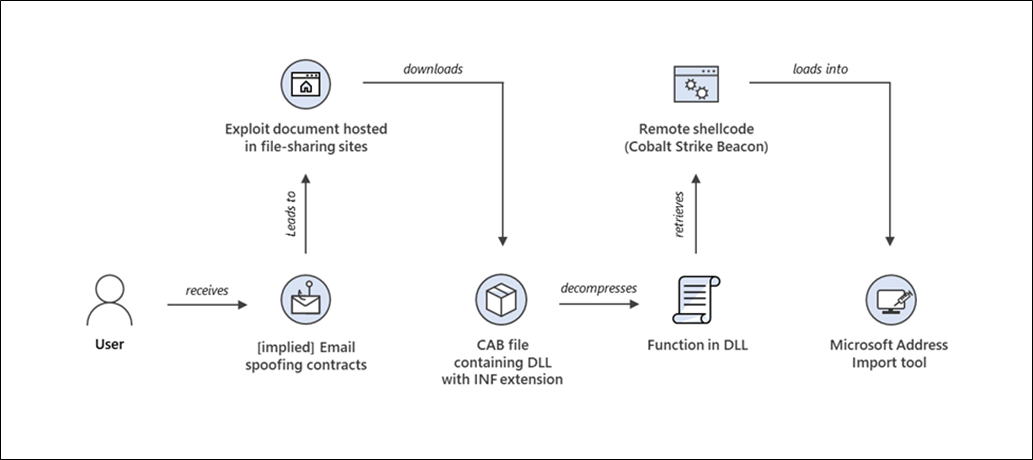
Microsoft released an advisory on a zero-day (CVE-2021-40444) vulnerability in Microsoft MSHTML that adversaries are actively exploiting through Microsoft Office documents. According to the company, this vulnerability has already been used in targeted attacks against Microsoft Office users. In an attempt to exploit this vulnerability, attackers create a document with a specially crafted object. If a user opens the document, MS Office will download and execute a malicious script.
Is Protected View Defended the attacks?
Even though Microsoft stated that Office opens documents from the internet in Protected View or Application Guard for Office, both of which prevent the current attack, the RTF attack vector is still open for exploitation. Adversaries can use several other bypasses for Protected View. Regardless, administrators should ensure they have Protected View enabled. Microsoft has provided workarounds as temporary mitigation until they release a patch.
The same attacks are still happening all over the world. We are currently seeing attempts to exploit the CVE-2021-40444 vulnerability targeting companies in various sectors includes the research and development sector, the energy sector, large industrial sectors, banking, medical technology development sectors, telecommunications, and the IT sector.
Microsoft has stated that both Microsoft Defender Antivirus and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint detect malicious files as long as the definitions are up-to-date. Organizations using only Microsoft Defender for Endpoint should ensure that they have placed their EDR in block mode.
Technical details
Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
Alerts with the following titles in the security center can indicate threat activity on your network:
- Possible exploitation of CVE-2021-40444 (requires Defender Antivirus as the Active AV) The following alerts might also indicate threat activity associated with this threat. These alerts, however, can be triggered by unrelated threat activity and are not monitored in the status cards provided with this report.
- Suspicious Behavior By Office Application (detects the anomalous process launches that happen in exploitation of this CVE, and other malicious behavior)
- Suspicious use of Control Panel item
Mitigations
- Turn on cloud-delivered protection to cover rapidly evolving attacker tools and techniques. Cloud-based machine learning protections block the majority of new and unknown variants.
- Use the latest Threat Intelligence information to keep up to date with TTPs used by threat actors.
- Businesses should use a security solution that provides vulnerability, patch management, and exploit prevention components, such as the Automatic Exploit Prevention component in Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business. The component monitors suspicious actions in applications and blocks malicious file execution.
- Use solutions like Metmox MDR-as-a-service and our Built to Suit Services service, which helps identify and stop an attack at an early stage before the attackers achieve their final goal.
- Metmox Solutioning teams help you with pre-implementation discovery, planning, design activities, and execution in the “Outcome-based - Built to Suit Services” model.
Preventing Exploit with METMOX’s EndPoint Security
- Based on different techniques used by the attackers, we have different processes to help our customers secure their organizations Metmox's endpoint security includes data security, network security, advanced threat prevention, forensics, endpoint detection, and response (EDR), and remote access VPN solutions.
- In addition to Incident response, vulnerability management, and various other security services, we provide threat hunting that exposes the Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and potential risks along with Machine-learning classification to detect zero-day threats in near real-time.
- Centralized endpoint management platform for greater visibility and simplify operations
We advise administrators to perform an enterprise-wide IoC sweep to check if their organizations have been targeted. METMOX is aware of targeted attacks using CVE-2021-40444, and our products protect against attacks leveraging the vulnerability. On September 7, 2021, Microsoft shared a partial workaround for the flaw, and only in 24 hours, they observed a rise in exploitation attempts within. Since no patch is yet available and bypasses are available for the mitigations, enterprise defenders must remain vigilant and proactively hunt for threats in their network.